Table of Contents
What is COVID-19?
COVID-19 stands for “coronavirus disease 2019″. It is caused by a disease called SARS-CoV-2. The virus emerged in late 2019 and quickly spread around the world.
People with COVID-19 may have a fever, cough, difficulty breathing, and other symptoms. Breathing problems occur when the infection affects the causes of pneumonia and the lungs.
For most people with COVID-19, symptoms are not severe, but others can be. Residents have been asked to stay home and isolate themselves from others in many areas. COVID restrictions have prevented people worldwide from traveling as well. The aim is to try and slow the spread of the virus.
This article discusses COVID-19 in children. Information on COVID-19 in adults is available in a separate document.
How Covid-19 Spreads?
The virus that causes COVID-19 is spread primarily from person to person, usually when an infected person sneezes or coughs near others. The virus is found in tiny particles from the infected person’s lungs and respiratory tract. These particles can move quickly through the air to other people nearby. In some cases, such as in confined spaces where the air is recirculated, the virus in these particles can spread to other people further away.
The virus can transfer easily between people in the same household. However, it can also be spread during encounters between people who talk to each other near, shake hands, hug each other, share food, or even sing together. Dining out increases the risk of infection because diners are usually close to each other and not wearing masks. Doctors also believe it is possible to become infected by touching a surface contaminated with the virus and then touching your mouth, eyes, or nose.
A person can get infected and spread the virus to others even without showing symptoms. It is why keeping a distance between people is one of the best ways to slow the virus’s spread.
It is strange whether this virus can enter a baby through breast milk if the mother is sick.
Can children get COVID-19? Yes. Children of all ages can contract COVID-19.
Also, children can pass the virus on to other people. It can be dangerous, especially for older people with other health problems.
Also read: 5 Fashion Trends for Spring in 2020
Are the Symptoms of COVID-19 Different in Children and Adults?
Not really. In adults, common symptoms include fever and cough. In more severe cases, patients may develop pneumonia and have difficulty breathing. Children with COVID-19 can also have these symptoms but are less likely to be very sick. Some children have no symptoms.
Other symptoms can also occur in children and adults. These can include sheer tiredness, chills, headache, muscle pain, sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, diarrhea, or vomiting. Babies with COVID-19 may have difficulty feeding. Rashes on the skin and other skin symptoms also have a virus. For example, some people with coronavirus have small red to purplish spots on their fingers and toes, but why or how often they occur is unclear.
Severe symptoms may be more common in children with health problems, including severe genetic or neurological disorders, congenital heart disease (from birth), sickle cell anemia, obesity, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, asthma, and more: other lung diseases, or a weakened immune system.
Can COVID-19 Cause Other Problems in Children?
It’s not common, but it can happen. In rare cases, children with COVID-19 have developed inflammation that has spread throughout the body. This inflammation can damage organs if the child is not shown to a doctor quickly. Experts use various expressions to describe this disease, including “multi-inflammatory syndrome in children” and “pediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome.” Symptoms may be similar to those of another condition called “Kawasaki disease.” They understand :
- Fever lasting more than 24 hours
- Stomach pain, vomiting, or diarrhea
- Rash
- Red eyes
- Headache
- Extreme fatigue, confusion, or irritability
- Breathing difficulties
Call your child’s doctor immediately if your kid develops one or more of these symptoms.
What Should I Do If My Kid Has Symptoms?
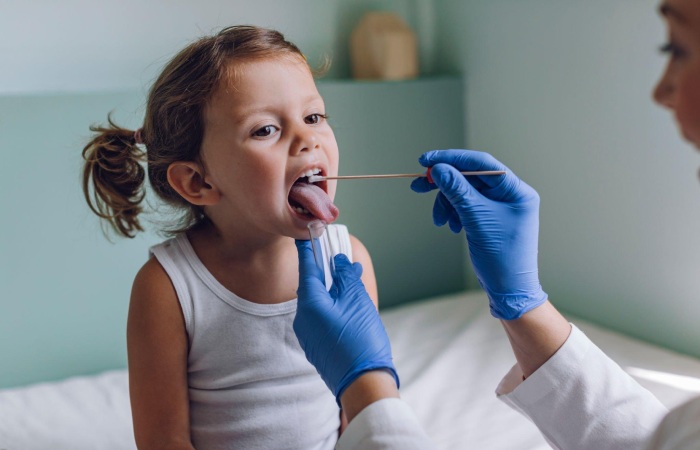
Call their doctor or nurse if your kid has a fever, cough, or other signs of COVID-19. They will tell you what to do and if your child needs to be seen by a healthcare professional.
If you care for your kid at home, your doctor or nurse will tell you what symptoms to watch out for. Some children with COVID-19 who have been showing signs for about a week have worsened their health. Your doctor or nurse can tell you when to call the office and the emergency room.
Here are the Symptoms
- has difficulty breathing;
- has pain or a feeling of tightness in the chest;
- appears disoriented or does not behave as usual;
- cannot wake up or stay awake.
- has severe stomach pain;
- has blue lips or face;
Call the doctor or nurse for advice if you have a baby and have difficulty feeding naturally.
Should my child test? If a doctor or nurse suspects that your child has COVID-19, he/she can take a swab with cotton swab in their nose or mouth to have them tested. These tests can help the doctor determine if your child has COVID-19 or another disease.
You must see a doctor or nurse to get a test in some areas. In others, organizations offer tests that are accessible to everyone. Depending on the lab, getting test results may take several days.
If you feel your child has been in close contact with someone who has COVID-19, they must diagnose, even if they do not show any symptoms. Call their doctor or nurse if unsure where to do this test. Whether or not your child is diagnose, he or she should remain in self-quarantine at home after exposure. It means staying home and away from other people as much as possible.
The safest thing to do is quarantine yourself for 14 days. Some public health departments may allow people to stop the quarantine earlier, especially if they test negative. If you are unsure how long the quarantine is for your child, contact your local public health unit or ask their doctor or nurse.
Even if your child stops quarantining sooner, after possible exposure, you should continue to monitor symptoms for 14 days. If he starts to develop symptoms, call his doctor or nurse immediately. Your child should also be cautious about wearing a mask and social distancing for 14 days.
How Is COVID-19 Treating in Children?
There is no known specific treatment for COVID-19. Most healthy children who suffer recover at home, and their condition usually improves within 1 to 2 weeks.
It is essential to keep your child at home and away from other people until your doctor or nurse tells you that he/she can resume normal activities. This decision will depend on how long it has been since the child’s symptoms first appeared and, in some cases, whether the test result is negative (showing that the virus is no longer in their body).
Doctors are currently studying several treatments to determine if they might be effective against COVID-19. Doctors sometimes recommend trying these treatments or participating in a clinical trial for hospitalized children. A clinical trial is a scientific study that tests new drugs to determine whether they work.

